The CSE graduates at UBT are expected to be able to adapt quickly to the trends in industry, to respond quickly to the needs of the market and to adopt an integrative approach in product and process development, and by virtue of their knowledge and experience in various disciplinary skills, be more competent team leaders. The graduates will be required to work in an industrial environment deploying advanced technology according to CSE principes as well as communicate with and provide a link between a specialist in particular area with the requirements of Kosovans businesses. They will also be able to make significant contributions in all stages compueter science and engeneering – from conceptualisation to final product design in a truly systemic approach wherin computer and engeneering sub systems are simultaneously integrated to provide solutions to real problems in industry and the soceity.
The Kosovo labour market demand for computer science and engeneering has been particulairly high in recent years. Based on a recent study of higher education graduate demand in economic and skill sectors (EC/LSE, 2015) in Western Balkans and Kosovo, ICT technicians and professionals is one of the most dynamic occupations in employment growth in Kosovo.
UBT on the other hand uses an indicator framework to assess demand for professionals and economic sectors. The indicator framework is composed of: (1) skill sectors employing most of professionals (to differentiative among all workers in the sector), (2) share of professionals’ distribution in all economic sectors (ISCO) and (3) job creation tendency in the past decade for the respective economic sector (NACE).
According to Kosovo Labour Force Survey (2015), the economic sectors with the highest share of employed professionals is in computer programming and manufacture of computers and electronics.
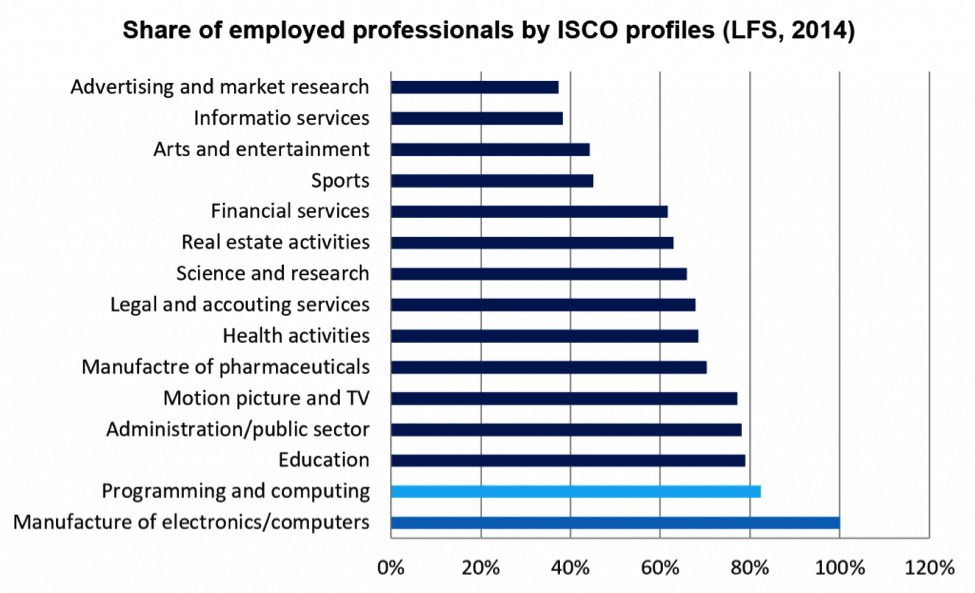
Adjusting to changing demands is usually rooted in knowledge used for creating the products and services being marketed. If the know-how is imported and the competitive advantage is built on cheap labour, there may be positive effects on income, employment and overall social welfare.Therefore, domestic knowledge growth and development are key to gain and retain competitiveness. A proxy used for the ability of economic sectors to adjust, innovate and remain competitive is the share of the employed in jobs which require high level skills in computer science and engeneering attainable dominantly through higher education qualifications as well as technical skills for applying knowledge in production environments.
Based on the job creation indicaton,despite its recent application and introduction to Kosovo economy, the ICT sector has created about 6500 new jobs.
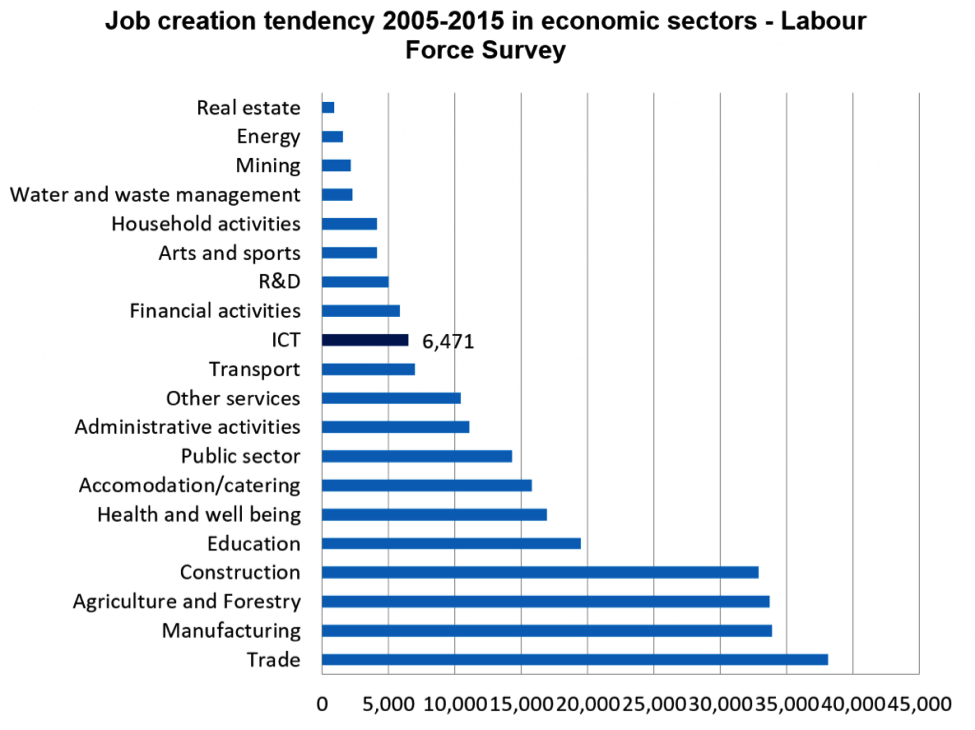
In summary, on the basis of Labour Force Survey computer programming and manufacture of computers and electronics are some of skill areas employing the highest share of professionals. Secondly, the professional occupations related to ICT find are applicable in about 30% of Kosovo economy mainly in industrial production, public administration, ICT, healthcare and personal services. The ICT sector has created around 6500 jobs in the past decade and according to economic projections another 10,000 new jobs will be created until 2025 (USAID, 2014).
The graduates will be able to work in varying professions and in varius economic sectors as :
- Business Information Manager– proposes plans and strategies for ICT integration in production, service delivery or administration.
- Database Administrator– analyses information management needs, designs, implements and maintains databases
- Developer– Builds ICT products and services according to clients’ demand
- Digital Media Specialist– creates websites and multimedia applications combining the power of digital technology with effective use of graphics, audio and video images.
- ICT Consultant– provides consultancy services to business and publication administration about how ICT provides value to competitivness, administration and service delivery.
- Network Manager– ensures the alignement of the network, including telecommunications and computer infrstructure to meet the organisations’communication.
- ICT Security Specialist– maintains organisations’ and clients network, database and information security
- Systems Administrator– administers ICT systems components in server, networks, database, web server and enterprise administrator.
- Technical Specialist– maintains and repairs hardware and software on clients’ premises